Preface#
In order to preview the junior year courses, I wanted to learn PyTorch in advance.
So I came across the amazing tutorial “Dive into Deep Learning”, and used it as a reference to complete the environment setup. Thanks to the contributors for their selfless dedication! Thanks♪(・ω・)ノ
This tutorial demonstrates the environment setup for running PyTorch deep learning on a Windows computer with a dedicated GPU using the WSL Ubuntu subsystem. As for why to use WSL, I found through testing that the performance is much stronger than Windows. Due to space limitations, the WSL installation process is omitted.
Installation#
Device:#
Windows 11: WSL-Ubuntu-22.04
1660ti-6g dedicated GPU
Miniconda Installation#
Download the corresponding Linux version using wget from the Miniconda official website
wget https://repo.anaconda.com/miniconda/Miniconda3-py310_23.3.1-0-Linux-x86_64.sh
Use the sh command for default installation
sh Miniconda3-py310_23.3.1-0-Linux-x86_64.sh -b
Initialize the environment
~/miniconda3/bin/conda init
You will be prompted to close this Terminal and open a new one.
Create a new environment, the name d2l can be changed.
conda create --name d2l python=3.9 -y
Activate the environment
conda activate d2l
Note that you need to run this command every time to switch to the d2l environment.
To exit the current environment: conda deactivate.
To completely delete the environment named d2l: conda remove -n d2l --all
CUDA Installation#
CUDA (official website) is NVIDIA's official deep learning toolkit, as shown in the WSL options. Run the download commands.

wget https://developer.download.nvidia.com/compute/cuda/repos/wsl-ubuntu/x86_64/cuda-wsl-ubuntu.pin
sudo mv cuda-wsl-ubuntu.pin /etc/apt/preferences.d/cuda-repository-pin-600
wget https://developer.download.nvidia.com/compute/cuda/12.1.1/local_installers/cuda-repo-wsl-ubuntu-12-1-local_12.1.1-1_amd64.deb
sudo dpkg -i cuda-repo-wsl-ubuntu-12-1-local_12.1.1-1_amd64.deb
sudo cp /var/cuda-repo-wsl-ubuntu-12-1-local/cuda-*-keyring.gpg /usr/share/keyrings/
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get -y install cuda
After adding, you need to update the ~/.bashrc file
sudo vi ~/.bashrc
Press i to enter insert mode, add the following code to the end of the file, and be sure to modify it to the corresponding version.
export PATH=/usr/local/cuda-12.1/bin${PATH:+:${PATH}}
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=/usr/local/cuda-12.1/lib64\
${LD_LIBRARY_PATH:+:${LD_LIBRARY_PATH}}
Press Esc, then type :wq and hit enter to save.
source ~/.bashrc
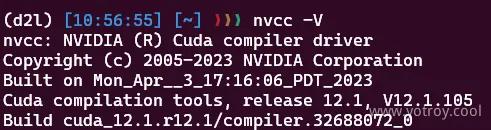
Run the following command, if the output is as shown in the image, then CUDA installation is successful.
nvcc -V
Install PyTorch Framework#
For the GPU version, you need to select it from the PyTorch official website. I downloaded the Preview version which happens to be compatible with CUDA 12.1 as shown in the image, but it also has good backward compatibility.
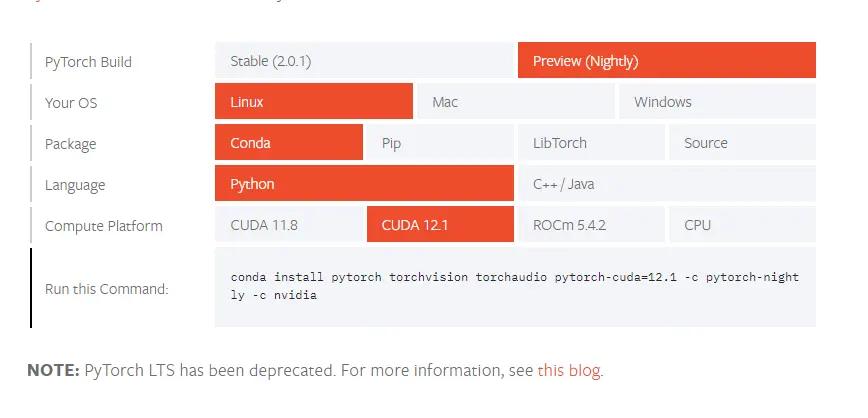
conda install pytorch torchvision torchaudio pytorch-cuda=12.1 -c pytorch-nightly -c nvidia
Download the d2l package
pip install d2l==0.17.6
GPU Testing#
Clone the test files
git clone https://github.com/pytorch/examples.git
cd examples/mnist/
Replace the content of the main.py file with the following:
from __future__ import print_function
import argparse
import torch
import time
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import torch.optim as optim
from torchvision import datasets, transforms
from torch.optim.lr_scheduler import StepLR
class Net(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Net, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(1, 32, 3, 1)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(32, 64, 3, 1)
self.dropout1 = nn.Dropout(0.25)
self.dropout2 = nn.Dropout(0.5)
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(9216, 128)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(128, 10)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv1(x)
x = F.relu(x)
x = self.conv2(x)
x = F.relu(x)
x = F.max_pool2d(x, 2)
x = self.dropout1(x)
x = torch.flatten(x, 1)
x = self.fc1(x)
x = F.relu(x)
x = self.dropout2(x)
x = self.fc2(x)
output = F.log_softmax(x, dim=1)
return output
def train(args, model, device, train_loader, optimizer, epoch):
model.train()
for batch_idx, (data, target) in enumerate(train_loader):
data, target = data.to(device), target.to(device)
optimizer.zero_grad()
output = model(data)
loss = F.nll_loss(output, target)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
if batch_idx % args.log_interval == 0:
print('Train Epoch: {} [{}/{} ({:.0f}%)]\tLoss: {:.6f}'.format(
epoch, batch_idx * len(data), len(train_loader.dataset),
100. * batch_idx / len(train_loader), loss.item()))
if args.dry_run:
break
def test(model, device, test_loader):
model.eval()
test_loss = 0
correct = 0
with torch.no_grad():
for data, target in test_loader:
data, target = data.to(device), target.to(device)
output = model(data)
test_loss += F.nll_loss(output, target, reduction='sum').item() # sum up batch loss
pred = output.argmax(dim=1, keepdim=True) # get the index of the max log-probability
correct += pred.eq(target.view_as(pred)).sum().item()
test_loss /= len(test_loader.dataset)
print('\nTest set: Average loss: {:.4f}, Accuracy: {}/{} ({:.0f}%)\n'.format(
test_loss, correct, len(test_loader.dataset),
100. * correct / len(test_loader.dataset)))
def main():
# Training settings
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='PyTorch MNIST Example')
parser.add_argument('--batch-size', type=int, default=64, metavar='N',
help='input batch size for training (default: 64)')
parser.add_argument('--test-batch-size', type=int, default=1000, metavar='N',
help='input batch size for testing (default: 1000)')
parser.add_argument('--epochs', type=int, default=14, metavar='N',
help='number of epochs to train (default: 14)')
parser.add_argument('--lr', type=float, default=1.0, metavar='LR',
help='learning rate (default: 1.0)')
parser.add_argument('--gamma', type=float, default=0.7, metavar='M',
help='Learning rate step gamma (default: 0.7)')
parser.add_argument('--no-cuda', action='store_true', default=False,
help='disables CUDA training')
parser.add_argument('--no-mps', action='store_true', default=False,
help='disables macOS GPU training')
parser.add_argument('--dry-run', action='store_true', default=False,
help='quickly check a single pass')
parser.add_argument('--seed', type=int, default=1, metavar='S',
help='random seed (default: 1)')
parser.add_argument('--log-interval', type=int, default=10, metavar='N',
help='how many batches to wait before logging training status')
parser.add_argument('--save-model', action='store_true', default=False,
help='For Saving the current Model')
args = parser.parse_args()
use_cuda = not args.no_cuda and torch.cuda.is_available()
use_mps = not args.no_mps and torch.backends.mps.is_available()
torch.manual_seed(args.seed)
if use_cuda:
device = torch.device("cuda")
elif use_mps:
device = torch.device("mps")
else:
device = torch.device("cpu")
train_kwargs = {'batch_size': args.batch_size}
test_kwargs = {'batch_size': args.test_batch_size}
if use_cuda:
cuda_kwargs = {'num_workers': 5, # Number of threads
'pin_memory': True,
'shuffle': True}
train_kwargs.update(cuda_kwargs)
test_kwargs.update(cuda_kwargs)
transform=transforms.Compose([
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize((0.1307,), (0.3081,))
])
dataset1 = datasets.MNIST('../data', train=True, download=True,
transform=transform)
dataset2 = datasets.MNIST('../data', train=False,
transform=transform)
train_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(dataset1,**train_kwargs)
test_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(dataset2, **test_kwargs)
model = Net().to(device)
optimizer = optim.Adadelta(model.parameters(), lr=args.lr)
scheduler = StepLR(optimizer, step_size=1, gamma=args.gamma)
start_time = time.time()
for epoch in range(1, args.epochs + 1):
train(args, model, device, train_loader, optimizer, epoch)
test(model, device, test_loader)
scheduler.step()
end_time = time.time()
total_time = end_time - start_time
print(f"Total time: {total_time:.2f} seconds.")
if args.save_model:
torch.save(model.state_dict(), "mnist_cnn.pt")
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
This uses 5 threads, which can be modified as needed.
Run the corresponding mode for speed testing; depending on the configuration, the CPU and GPU running codes may be exactly opposite.
$ python main.py # CPU mode
$ CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=2 python main.py # GPU mode
Source and reference for the test code:
pytorch/examples - github
Deep Learning: Performance Comparison of Windows 11 VS WSL2 VS Ubuntu, PyTorch 2.0 Performance Testing!
Completion!#
The environment setup is complete, and I will continue to follow “Dive into Deep Learning”.
mkdir d2l-zh && cd d2l-zh
curl https://zh-v2.d2l.ai/d2l-zh-2.0.0.zip -o d2l-zh.zip
unzip d2l-zh.zip && rm d2l-zh.zip
cd pytorch
。。。。。